Japan is a unique country. In many ways, it is the people who make it unique. With an almost complete absence of mineral resources, in a climate not very favorable for agriculture, and having survived quite serious losses in World War II, the Japanese managed to preserve their national identity and create one of the most powerful economies in the world. It is also worth considering that Japan is one of the few highly developed countries located exclusively on islands. The Land of the Rising Sun is the fourth largest island nation in the world by area. In terms of territory size, it is second only to Indonesia, Madagascar and Papua New Guinea.
There are 6,852 islands belonging to Japan, all of which are part of the Japanese archipelago. People live on only 430 islands, but the vast majority of the population is concentrated on just the four largest islands. Each of them is worthy of a separate story.
Honshu
Geography and demographics
The island of Honshu is larger in size than all its neighbors in the archipelago. With an area of 228 thousand square meters. km, this island would not get lost even in the company of independent states. Honshu is only slightly smaller in area than Romania, but larger than Belarus, Uruguay or Syria. And in terms of population - more than 100 million people - Honshu would confidently enter the top twenty countries, ahead of Egypt, Vietnam and Germany. The largest island, which covers 60% of the country's territory, is home to 80% of the Japanese. The territory of Honshu is divided into 34 prefectures, which are combined into five regions.
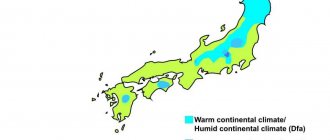
Corresponds to the size of the territory and the variety of climatic conditions on Honshu. The southeastern part of the island, protected from cold winds by mountains (the legendary Fuji is also located on Honshu), blissfully enjoys a subtropical climate on the shores of the Pacific Ocean. In the north-west of the island the climate is quite sharply continental
Tokyo
The capital of Japan is located in the southeast of Honshu. The population of Tokyo is about 14 million people. It is known that people lived in Tokyo back in the Stone Age, but the history of the city dates back to the 12th century, when a fort called Edo was built here. Tokyo became the capital of the state in 1868. In the 20th century, Tokyo suffered serious damage twice - in the 20s due to an earthquake, and in the 40s due to American bombing. However, just 20 years after the end of World War II, Tokyo became the largest metropolis with a highly developed industry.
Tokyo's gross domestic product exceeds one and a half trillion dollars, but much of the city's output cannot be touched. The Japanese capital is, first of all, a financial and administrative center. Due to the desire of large companies to have offices in Tokyo, living in the city is very expensive. This applies to land, housing, and the overall cost of living. Tokyo has been recognized as the most expensive city in the world for many years in a row, only in recent years losing this dubious honor to Singapore, Hong Kong and Zurich.
Yokohama
Yokohama, with a population of 3.7 million, is the second city in Japan according to this criterion. It is interesting that the two most populated Japanese metropolises are de jure separated by only about 30 kilometers, although in practice Tokyo and Yokohama merge into one agglomeration.
The history of Yokohama is inextricably linked with the port. As soon as Japan opened to the outside world in the 19th century, a port appeared on the site of two fishing villages. He gave impetus to the development of the city. This development was not slowed down even by the earthquake of 1923, which destroyed 60,000 houses and claimed 20,000 lives. Yokohama has become a powerful transport hub where sea and railway routes intersect.
The city is home to many high-tech enterprises, as well as the offices of several of Japan's largest corporations. The main attraction of Yokohama is the suspension road bridge connecting the shores of Tokyo Bay.
Biggest
The largest and most famous of the list of Japanese islands is Honshu. It contains most of the country. Let's talk, what else is interesting about him? First of all, because the main cities familiar to all of us are located here - Tokyo, Hiroshima, Osaka, Kyoto and others. The most famous and popular in Japan, the sacred Mount Fuji (富士山・the Japanese call it “Fuji”, and “yama” is “mountain” in Japanese), also in Honshu. By the way, this is a real volcano that is in dormant mode.
The island is full of different volcanoes, some of them are quite creepy. For example, the Osoreyama volcano is “mountain of fear.” Why? - you ask. After all, it is not so high, only 879 meters. The fact is that the mountain is almost devoid of vegetation, gray and lifeless. Seething sulfur springs spread their suffocating smell, and there are terrifying abysses.
Imagine this picture. And now further. There is an old temple here; since ancient times, pilgrims, people with wounded souls have come to this mountain. Many have found their peace here. They say that the souls of the dead fly here. Mount Osoreyama (“osore” means “fear” in Japanese) is considered by many sources to be the gateway to hell. Sometimes, special rituals are held here to communicate with the spirits of ancestors.
Another pride of Honshu is a magnificent national park called Fuji Hakone Izu. It is more attractive to ecotourists seeking the beauty and purity of untouched nature. Honshu is especially attractive in spring, when peonies and Japanese azaleas (sometimes called "Japanese rhododendrons") bloom. Also on this island is the sacred Itsukushima Temple, the gates of which are located far from the shore (pictured).
Hokkaido
Geography, demography and economics
The second largest island in the Japanese archipelago, Hokkaido, is the most un-Japanese of all the Japanese islands. It is located farthest north of all, so, according to the Japanese, it is terribly cold. It's no joke, the average annual temperature is only +8. Accordingly, the population density in Hokkaido is minimal by Japanese standards - 66 people per square kilometer (in Honshu, for example, this figure is 439).
Hokkaido in Japan is about the same as Alaska in the USA. The people live quite poorly, but look down on other Japanese. Firstly, because of the climate, and secondly, because the majority of the population of Hokkaido outside the largest city of Sapporo is engaged in productive work, rather than being classified as white-collar workers. On the island they engage in agriculture and fishing, mine coal and iron ore, cut timber and produce paper.
Sapporo
The largest city and administrative center of Hokkaido is Sapporo. This city is best known throughout the world for hosting the 1972 Winter Olympics. Sapporo (pop. 2 million) is more like the rest of Japan. The majority of the city's population is employed in the service sector. Sapporo is the center of a large climatic resort and winter sports. The snow festival, held every year in early February, attracts millions of visitors.
Island state
From the school geography course, we know that Japan is located on islands. All of them are located in the Pacific Ocean, and the number exceeds 6,000 pieces! These include large main islands and very small islands where no one lives. The largest ones are called the Japanese archipelago. I will present a list of Japanese islands from the largest in descending order.
- Honshu
- Northern: Hokkaido
- Kyushu
- Shikoku
- Southern: o. Okinawa, Minamitori and Bonin Islands
In the photo I indicated that the largest four islands, the islets of the Ryukyu archipelago (including Okinawa), are located a little further away, a little lower and the island of Kyushu. Japan also includes quite a few small islands, half of which are uninhabited. It turns out that the country owns territory on land and sea. All its parts differ in climate, culture, cuisine, attractions and even language dialects.
Kyushu
Geography, demography and economics
Some historians believe that Japanese civilization began on the island of Kyushu. The relief of the third largest Japanese island is highly rugged. There are no too high mountains, but hardly a quarter of the territory of Kyushu can be classified as plains.
The climate on the southernmost of the large Japanese islands is subtropical and mild. Kyushu has many rivers and underground springs, and the island is rich in diverse vegetation.
More than 12 million people live on the island. With an island area of 40.5 thousand square meters. km, the population density is almost 300 people per square meter. km.
Production in Kyushu is quite clearly divided geographically - industry is concentrated in the north of the island, agriculture in the south. Chemistry, metallurgy and metalworking are well developed. Farmers grow industrial crops, rice and raise livestock.
Fukuoka
The city of Fukuoka was a port connecting Japan to the continent back in the first millennium AD. Accordingly, the city developed as a commercial and cultural center. In the middle of the last century, Fukuoka also became an industrial center. These same industries are developed in the city today.
In addition, the city with a population of 1.5 million people has enterprises producing computers and telecommunications equipment, mechanical engineering products and electrical goods. Fukuoka is the junction of almost all the island's railways and roads.
Bonin Islands
A small group lying between Japan and the Mariana Islands. They are also called the Ogasawara Islands. They have collected more than a hundred species of interesting plants and insects. Local residents live on only two islands; there are just over two thousand people. They grow bananas and pineapples and harvest wood.
Ogasawara is not spoiled by civilization, so people go there with pleasure. Vacationers are busy looking at colorful reefs and colorful tropical fish. On special excursions they watch dolphins, whales and turtles. Time seems to stop there.
Shikoku
Geography and demographics
Shikoku Island boasts the title of the smallest of the large Japanese islands. The mild climate and developed river network favor the development of agriculture, so the island is underdeveloped industrially. Industry, which is based on metallurgy and shipbuilding, is concentrated in the north of Shikoku. In the south, where two harvests can be harvested a year, people are mainly engaged in agriculture.
On an island with an area of 18.8 thousand square meters. km. 4 million people live. The population is gradually aging and shrinking - young people are leaving Shikoku, moving to more developed regions of Japan. Even the construction of bridges between Shikoku and the island of Honshu does not help the outflow of population.
Matsuyama
Matsuyama is not only the largest city on the island of Shikoku. This is the real capital of haiku. Six times a year, the city holds a competition for the best traditional Japanese poetry. Every year, up to 50,000 poetic works participate in competitions.
Matsuyama is another of the oldest cities in Japan, which became part of the state back in the 4th century AD. After a series of historical upheavals, the city became the center of the prefecture, which sharply increased its status.
Nowadays, enterprises in the paper, textile and engineering industries, as well as petrochemical production, operate in Matsuyama. The city generates a lot of income from tourists visiting historical castles, temples, and pilgrims - 8 Matsuyama temples are included in the famous Buddhist pilgrimage route 140 kilometers long.
Ryukyu Archipelago
Once upon a time, or rather in the 15th century, the Kingdom of Ryukyu was an independent state. But later, after being captured by the Satsuma clan, the country came under the subordination of Japan. After this, almost 200 years later, territorial reform was introduced on the territory of the Land of the Rising Sun (during the Meiji era), from that moment, “clans” became “prefectures”. These events also influenced the fate of the Kingdom, as a result of which, a few years later, the Ryukyu Kingdom ceased to officially exist, and Okinawa Prefecture appeared, which we know to this day.
The island of Okinawa, not typical for Japan, delights tourists with its turquoise sea, hot climate and wonderful cuisine. Okinawa is like the Japanese “Hawaii”, heavenly climate, white sand, amazing sea. And of course, amazing delicacies and other goodies of Japanese cuisine. Every year many tourists come here.
What else is Okinawa rich in?
- Fabulous coral reefs
- Mysterious caves
- Snow-white clean beaches
- Amazing architectural
- Enchanting nature
- Beautiful ceramics and textiles
- And there is also some kind of music here. Melodious and beautiful. Listening to it, you can enjoy the sunset and enjoy life.
There is a particularly interesting place on the island - the Ancient Ryukyu amusement park. If you want to touch the history of the island yourself, then come here. Here you will be dressed in a kimono and given the opportunity to try ancient crafts. You can imagine yourself as a weaver or potter. Eat national dishes and listen to funny songs.
Minamitori
He's Fr. Marcus is the easternmost island, triangular in shape and very small. Its size is a little more than 1.2 km. An island of volcanic origin located in the Pacific Ocean. There are no permanent residents, but there are employees - about 10 people employed at the meteorological station and other work. It must be said that although this piece of land is tiny in size, the territorial waters surrounding it are quite spacious and have a rich and interesting fauna.
With this, I conclude today's geographical excursion. If I find out anything else interesting, I will definitely share it with you. Thank you for reading the blog. Share what you learn with your friends on social networks. Subscribe to updates if you haven't already. Have a good day!
Lika Raido
What else you need to know about the Japanese archipelago: interesting facts
- Hashima Island in the mid-20th century was considered one of the most densely populated places on the planet, where in the residential area the population density reached 140 thousand people per km². Such indicators were associated with the presence of coal mines and active mining. When the mines closed completely in 1974, Hashima went from the most densely populated area to an uninhabited ghost island in a matter of weeks.
Hashima Island
- On the island of Honshu at the foot of Mount Fuji there is a suicide forest, where, for anomalous reasons, all people who decide to commit suicide are drawn. In the forest itself there is a strong magnetic field, which prevents compasses from working normally and, perhaps, somehow affects human consciousness.
Suicide Forest at Mount Fuji
- One of the UNESCO World Heritage Sites is the island of Yakushima, located on the map slightly south of Kyushu. This is a unique example of preserved nature. Cedar grows here, the age of which exceeds 7000 years.
Yakushima Island
- The most dangerous volcano in the world is located on the Japanese island of Iwo Jima. Volcanologists believe that if it erupts, it can lead to the formation of a 25-meter tsunami that will devastate southern Japan and coastal China.
Iwo Jima Island
- Okinawa has the second largest oceanarium in the world, which has an area of 19 thousand m² and holds 10 thousand m³ of water. Here you can observe the life of almost all the inhabitants of the ocean - from small aquarium fish to terrifying whale sharks.
Oceanarium on the island of Okinawa
Despite the fact that the Japanese archipelago does not have ideal living conditions, local residents have learned to use the opportunities presented to them with maximum efficiency. This is likely why today Japan is considered a leader in many areas of life, having one of the highest levels of economic development.